Xu, J., Heumüller, T., Le Corre, V.M., Barabash, A., Félix, R., Frisch, J., Bär, M., Brabec, C.J.
Joule 8, 1–15, 2024
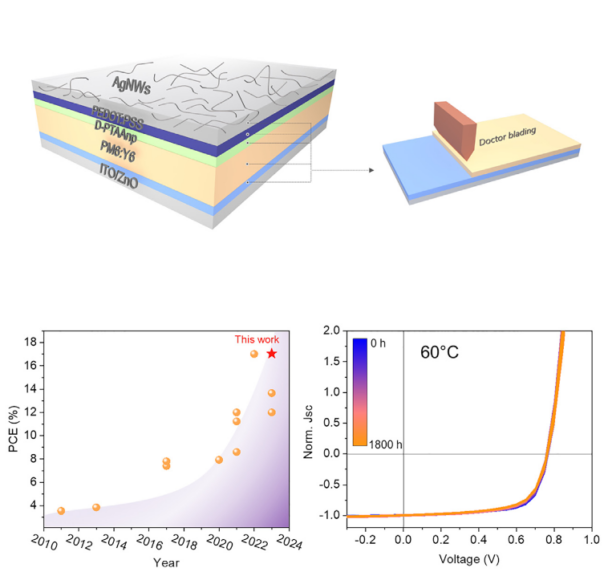
All-solution-processed organic photovoltaic (OPV) cells allow cost- and energy-effective fabrication methods for large-area devices. Despite significant progress on laboratory-scale devices, there is still a lack of interface materials that can be solution processed on top of the active layer, are compatible with novel non-fullerene acceptors (NFAs), and also provide sufficient long-term stability. We developed a novel interface layer concept, where alcohol-based organic polymer nanoparticles can be processed on top of a polymer-NFA active layer and doped to achieve a quasi-Ohmic hole contact. Moreover, poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene):poly(styrenesulfonate) (PEDOT:PSS) is processed as a second layer, forming a bilayer solution-processed hole transporting layer (HTL),
providing an industrially relevant inverted architecture with a protective PEDOT:PSS layer on top. Most importantly, exceptional stability is observed. PM6:Y6 devices with the bilayer HTL are demonstrated to maintain 93% of their initial efficiency for 1,800 h under continuous solar cell operation at 60C.
Xu, J., Heumüller, T., Le Corre, V.M., Barabash, A., Félix, R., Frisch, J., Bär, M., Brabec, C.J.
Joule 8, 1–15, 2024
All-solution-processed organic photovoltaic (OPV) cells allow cost- and energy-effective fabrication methods for large-area devices. Despite significant progress on laboratory-scale devices, there is still a lack of interface materials that can be solution processed on top of the active layer, are compatible with novel non-fullerene acceptors (NFAs), and also provide sufficient long-term stability. We developed a novel interface layer concept, where alcohol-based organic polymer nanoparticles can be processed on top of a polymer-NFA active layer and doped to achieve a quasi-Ohmic hole contact. Moreover, poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene):poly(styrenesulfonate) (PEDOT:PSS) is processed as a second layer, forming a bilayer solution-processed hole transporting layer (HTL),
providing an industrially relevant inverted architecture with a protective PEDOT:PSS layer on top. Most importantly, exceptional stability is observed. PM6:Y6 devices with the bilayer HTL are demonstrated to maintain 93% of their initial efficiency for 1,800 h under continuous solar cell operation at 60C.